Cirrhosis of Liver
Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver)

Causes
There are many causes of ‘scarring’ of the liver { (Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver) of Liver)}. The common causes are heavy alcohol drinking and infection with the hepatitis C virus. Less common causes include:
- Chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus. Worldwide, this is the most common cause of Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver) of liver.
- Autoimmune hepatitis The immune system normally makes antibodies to attack bacteria, viruses and other germs. In people with autoimmune diseases, the immune system makes antibodies against part(s) of the body. Something triggers the immune system to make these autoantibodies but the trigger is not known. In autoimmune hepatitis, the immune system makes antibodies against liver cells, which can lead to damage and Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver).
- Diseases that cause blockage of the bile ducts can cause back pressure and damage to the liver cells. For example, primary biliary Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver), sclerosing cholangitis, and congenital problems of the bile ducts.
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) This is a condition which causes fat to build up in the liver. This can lead to scarring and Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver). Being overweight/obese increases your risk of developing NASH.
- Severe reactions to certain medicines.
- Certain poisons and environmental toxins.
- Certain infections caused by bacteria and parasites which are usually found only in tropical countries. Parasites are living things (organisms) that live within, or on, another organism.
- Severe heart failure which can cause back pressure of blood and congestion in the liver.

Some rare inherited diseases which can cause damage to liver cells. For example
- HaemochromatosisThis is a condition which causes an abnormal build-up of iron in the liver and other parts of the body.
- Wilson’s diseaseThis is a condition which causes an abnormal build-up of copper in the liver and other parts of the body.
- Fails to make enough proteins such as albumin that help to regulate the fluid composition in the bloodstream and body.
- Fails to make enough chemicals needed for blood clotting.
- Is less able to process waste chemicals in the body such as bilirubin. So, these may build up in the body.
- Is less able to process medicines, toxins and other chemicals which may then build up in the body.
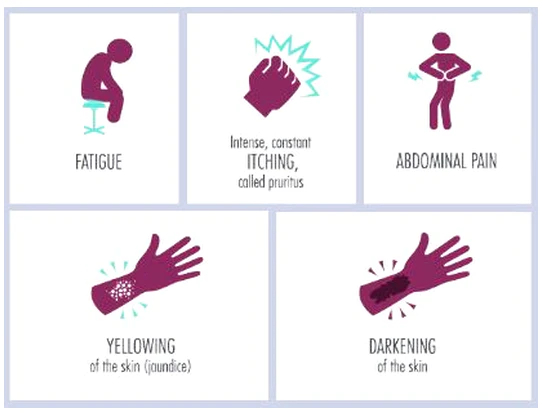
Therefore, the symptoms that may develop include:
- Tiredness and weakness.
- Fluid which leaks from the bloodstream and builds up in the legs (oedema) and tummy (abdomen) – called ascites.
- Loss of appetite, feeling sick (nausea) and being sick (vomiting).
- Weight loss (although you may put on weight if you retain a lot of fluid).
- A tendency to bleed and bruise more easily.
- Yellowing of the skin or the whites of the eyes (jaundice) due to a build-up of bilirubin.
- Itch due to a build-up of toxins.
- Mental health changes which can develop in severe cases as toxins build up in the bloodstream and affect the brain. This can cause changes to your personality and behaviour, confusion, forgetfulness and difficulty concentrating. Eventually it can lead to loss of consciousness and hepatic coma. These changes are known as hepatic encephalopathy.
Also, the scar tissue restricts the flow of blood through the liver. As the Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver) becomes worse, this causes back pressure in the portal vein (known as portal hypertension). The portal vein is the vein that takes blood from the gut to the liver – it contains digested foods. Increased pressure in this vein can cause swellings (varices) to develop in the branches of the vein in the lining of the gullet (oesophagus) and stomach. These varices have a tendency to bleed easily into the gut. If a bleed occurs, you may vomit blood or pass blood with your stools (faeces).
Care and treatment for Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver)
The first aim of treatment is to prevent further liver scarring or to slow the progression of the scarring process. Second step is to reverse the scarring process through Hepatoprotective Herbs. Treatments that may be advised include the following.
Stop drinking alcohol
Whatever the cause of Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver), you should stop drinking alcohol completely. Drinking alcohol will increase the rate of progression of Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver) from whatever cause.
Be cautious when taking medicines
Always tell your doctor or pharmacist that you have Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver) if you take any prescribed or over-the-counter medicines. Some medicines that are processed in the liver may need their dose adjusted if you have liver problems, or even should not be used at all.
Treatment for underlying causes
Some of the underlying causes of Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver) can be treated. This may slow down, or halt, the progression of Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver). For example: • Not drinking alcohol if alcohol is the cause. • Interferon and other medication may be used to treat viral hepatitis. • Steroid medicines or other immunosuppressant medicines may be used to treat autoimmune diseases causing liver damage. • Regular removal of a pint or so of blood can remove excess iron which occurs in haemochromatosis.
Treatment to ease symptoms and prevent complications
Various treatments may be advised, depending on the severity of the Yakridalyaudar (Cirrhosis of Liver) and the symptoms that develop. For example: • Adequate food intake (including calories and protein) and regular exercise are important to prevent excessive weight loss and muscle wasting. • A low-sodium diet or ‘water’ tablets (diuretics) to reduce fluid accumulating in the body. • Medicines to reduce itch.
Ayurvedic Remedies:
For Ayurvedic treatment of ‘Cirrhosis of liver’ please contact our physicians at:
Best Ayurveda Clinic
- +1-416-804-1500
- +1-647-276-1111
- info@bestayurveda.ca
- 2250 Bovaird Dr. E, Unit 316, Brampton ON L6R0W3
